Hooke's Law - Spring Constant
Hooke's Law - Measuring the spring constant with Capstone
Hang a force sensor from a bench stand, hang a spring with a mass hanger with 50g mass on it, and place a motion sensor on the floor directly below the mass hanger.
Tarre the force sensor so that this beginning mass-spring combination is the zero point (This mass was chosen so that it slightly stretches the spring so that no adjacent coils are touching). Place the motion sensor switch in its Wide position.
Start Capstone and open the file: K:\Physics\Demonstrations\Hookes Law.cap
1. Click on <Preview>. The Force should be 0.0 and the Absolute Position at the upper right should be about 1 m. Record this displacement. Click on <Stop>.
2. Open the Calculator and edit the formula by subtracting off the initial Absolute Displacement you recorded above. For example:
Displacement = [Position(m)] + 1.01
<Accept>
Close the Calculator
This makes the starting displacement for our "zero" mass be "zero" displacement.
3. Again click on <Preview> and click on <Keep Sample>
This saves the data in row one of the table and moves to the next row.
4. Add 0.100 kg to the weight hanger and click on <Keep Sample>. Try to keep the mass hanger is balance so that it hangs straight.
Continue on in steps of 0.100 kg until you get to about 0.800 kg.
5. After keeping the last data point, click on <Stop>
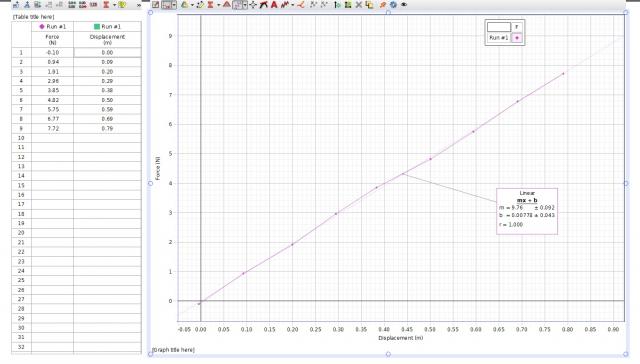
6. Select Curve Fit and then Linear: mx + b
Required Equipment